- bdttonyjiao@hotmail.com
- +86 +8615081115902
- 9-1-701 TonfuTown Stadt Shijiahzuang Provinz Hebei China
Mai . 26, 2025 16:04 Zurück zur Liste
Understanding Blood Collection Tubes: Focus on Plain Tubes and EDTA Tubes
In clinical diagnostics, accurate laboratory test results begin with the right sample collection. Among the most commonly used tools in phlebotomy are the plain tube and the EDTA tube, each designed for specific testing purposes. This article explores the functions, components, and applications of both types, with a special emphasis on plain tube clot activator, serum collection, and appropriate usage contexts.
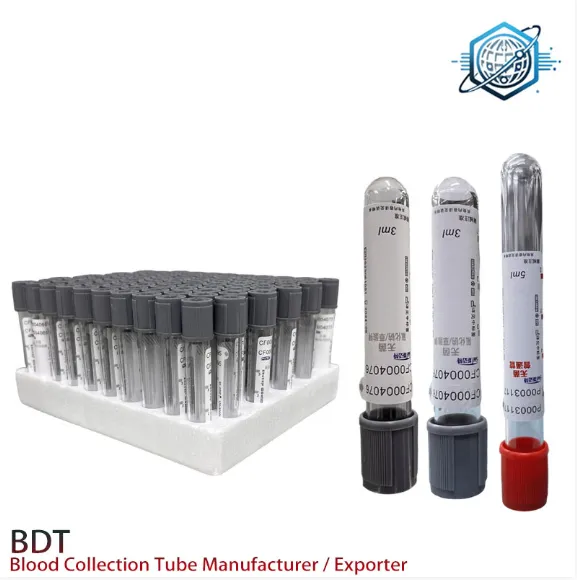

What is a Plain Tube Used For?
A plain tube is a type of blood collection tube that does not contain any anticoagulant. This means that when blood is drawn into a plain tube, it is allowed to clot naturally. After clotting, the sample can be centrifuged to separate the serum from the clot. The serum is the clear, yellowish fluid that remains after clotting and is free of blood cells and clotting factors.
Plain tubes are used for:
Biochemistry tests (e.g., liver function tests, renal profile)
Serology (e.g., HIV, Hepatitis B and C)
Immunology
Electrolyte analysis
Because there are no anticoagulants, plain tubes are ideal for any test that requires serum, as opposed to plasma or whole blood.
Plain Tube Clot Activator and Serum Separation
In some settings, laboratories opt for a plain tube with clot activator. A clot activator is a substance added to the interior of the tube to speed up the clotting process. Common clot activators include silica particles that promote rapid clot formation within 15–30 minutes, significantly reducing waiting time before centrifugation.
Using a plain tube clot activator enhances efficiency and is especially useful in high-throughput labs where time is critical. Once the blood clots, the tube is centrifuged, and serum is collected for further analysis. This serum is then used in a wide range of diagnostic tests due to its purity and stability.
It's important to note that while plain tubes with clot activator promote faster processing, they do not interfere with test results, making them a popular choice in modern laboratories.
EDTA Tube vs. Plain Tube
While the plain tube is used to obtain serum, the EDTA tube is used to obtain whole blood or plasma. The EDTA tube contains ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid (EDTA), an anticoagulant that prevents blood from clotting by binding to calcium ions. This property makes EDTA tubes ideal for tests that require intact blood cells.
EDTA tubes are used for:
Complete blood count (CBC)
Blood smears and differential counts
Hemoglobin and hematocrit testing
Molecular and DNA testing (PCR)
Unlike the plain tube, the EDTA tube keeps blood in its whole form, allowing laboratories to study blood cells and plasma-based components. These tubes are usually color-coded with lavender or purple caps.
Understanding the proper usage and contents of blood collection tubes is essential for accurate diagnostic outcomes. The plain tube is favored for its ability to yield high-quality serum, especially when enhanced with a clot activator. In contrast, the EDTA tube is indispensable in hematology for preserving cellular components and preventing coagulation.
Whether you’re using a plain tube used for routine biochemical tests or an EDTA tube for complete blood counts, knowing the purpose and function of each ensures that the right sample is collected for the right test—leading to reliable and timely medical decisions.
-
The Ultimate Guide to Choosing the Safest Cat Heating Pad
NachrichtJul.25,2025 -
The Science Behind Self-Heating Pet Mat
NachrichtJul.25,2025 -
The Science Behind Salt Heaters
NachrichtJul.25,2025 -
The Perfect Temperature: How Reptile Heat Mats Improve Pet Health
NachrichtJul.25,2025 -
The Cozy Canine: How a Dog Heating Pad Keeps Pets Warm
NachrichtJul.25,2025 -
Pet Heating Pad: The Ultimate Guide
NachrichtJul.25,2025