- bdttonyjiao@hotmail.com
- +86 +8615081115902
- 9-1-701 TonfuTown Shijiahzuang City Hebei provints Hiina
Practical Applications of Venous Blood Collection Tubes in Healthcare
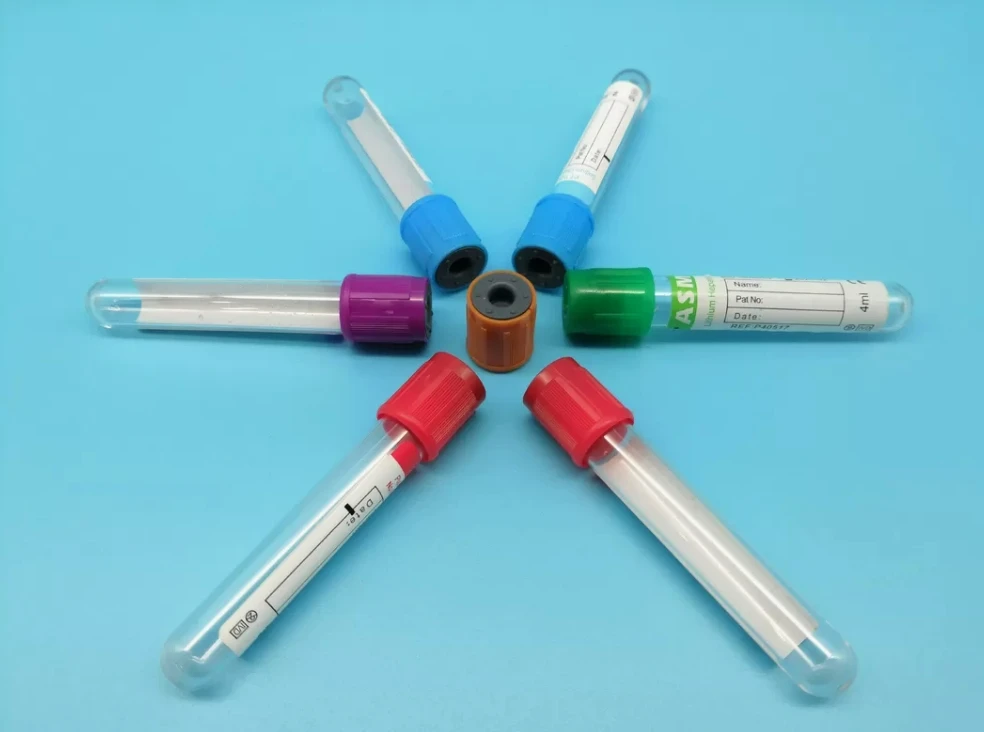
Venous blood collection tubes, also known as vacutainer tubes, are essential medical devices in modern healthcare, playing a pivotal role in various diagnostic and therapeutic procedures. Designed with specialized additives and color-coded stoppers for different testing requirements, these tubes ensure accurate and reliable blood sample collection. This article explores their practical applications across clinical settings, highlighting their significance in disease diagnosis, monitoring, and treatment.
Biochemical and Metabolic Assessments of Venous Blood Collection Tubes
Venous blood collection tubes, precisely powering medical testing. From disease diagnosis to research exploration, they safeguard the health frontlines in all aspects.
Key Considerations for Optimal Use of Blood Collection Tubes
Proper Tube Selection: Matching tube type (additive, volume, color) to the test requirement is vital to avoid pre-analytical errors. Sample Handling: Adhering to collection protocols (e.g., inversion for anticoagulant mixing, timely centrifugation) maintains sample integrity. Regulatory Compliance: Tubes must meet international standards (e.g., ISO 23614) for safety and traceability.
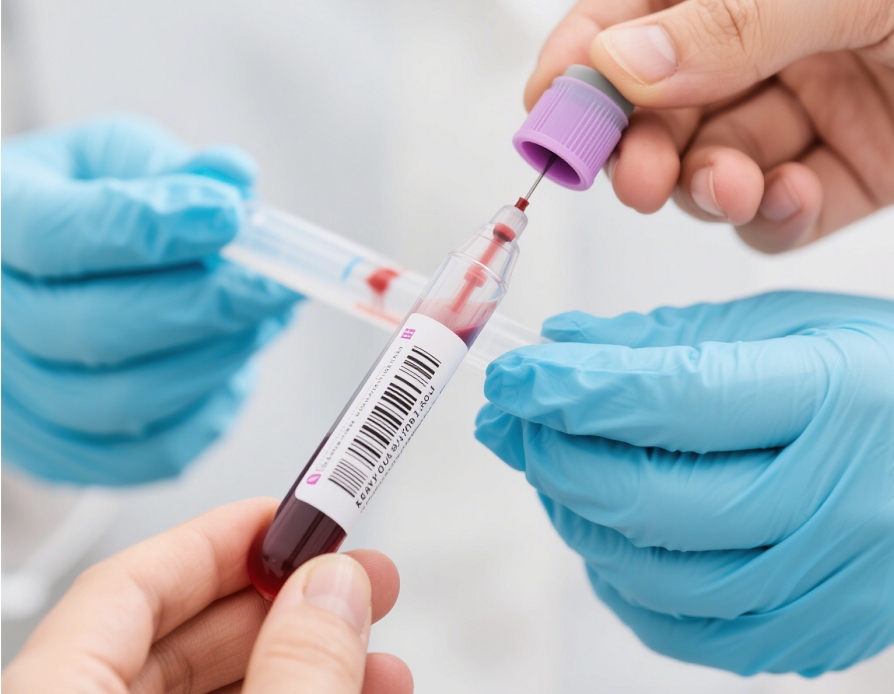
Clinical Advantages of Blood Collection Tubes
Minimally Invasive Reduces pain, anxiety, and complications (e.g., phlebitis, hematoma). Small Sample Volume Suitable for patients with limited blood volume (e.g., neonates, anemia patients). Ease of Self-Collection Empowers patients (e.g., diabetics) to monitor health at home. Versatile Additives Tubes with EDTA, heparin, or no additives meet diverse testing requirements. Cost-Effective Lower equipment and training costs compared to venous blood collection.
Join Our Newsletter
Subscribe to the weekly newsletter for all the latest updates