May . 09, 2025 09:34 Back to list
Understanding Plain Serum Tubes: A Vital Component of Blood Collection for Laboratory Tests
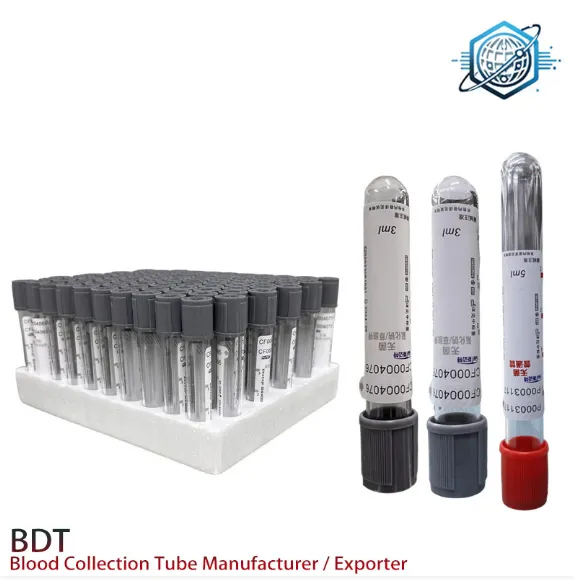
Blood collection tubes are essential tools in clinical and laboratory settings, helping to ensure accurate and reliable test results. Among the various types of blood collection tubes, plain serum tubes are often used for tests that require serum, which is the liquid portion of blood after the clotting process. Understanding the differences between plain serum blood tubes, plain serum tubes, and other tubes like the plain tube and EDTA tube combination is essential for accurate sample processing. This article will explore the use of plain serum tubes, their applications, and their significance in blood testing.

The Role of Plain Serum Tubes in Blood Testing
Plain Serum Blood Tube
A plain serum blood tube is a specialized type of blood collection tube that is commonly used in laboratory settings. It does not contain any anticoagulants or additives, meaning the blood collected in these tubes will naturally clot. Once the blood clots, the liquid portion of the blood, known as serum, can be separated from the solid components such as red blood cells and white blood cells through centrifugation.
These tubes are typically used for tests that require serum for analysis, such as blood chemistry panels, hormone level tests, and serological testing. Because they allow the blood to clot, the plain serum blood tube is essential for obtaining serum samples, which are used to measure various components in the blood, including electrolytes, proteins, enzymes, and other molecules. The absence of additives in the plain serum blood tube ensures that the serum remains uncontaminated, allowing for accurate test results.
Plain Serum Tube
The plain serum tube is similar to the plain serum blood tube but may be more broadly referred to by different manufacturers or in various settings. These tubes come in different sizes and are designed with a stopper that allows for the collection of a specific volume of blood. After collection, the blood will begin to clot naturally within the tube.
Once the blood has clotted, the plain serum tube is often subjected to centrifugation, which separates the serum from the clot. The resulting serum is then analyzed for various biochemical markers. These tubes are crucial in laboratory settings for tests where the liquid portion of blood, or serum, is needed, such as in liver function tests, kidney function tests, and metabolic panels.
Unlike EDTA tubes, which are used to prevent clotting and are essential for tests requiring whole blood or plasma, plain serum tubes are used specifically for tests that require a clear, serum sample after the blood has clotted.
Differences Between Plain Tubes and EDTA Tubes
Plain Tube and EDTA Tube
Both plain tubes and EDTA tubes are commonly used in medical laboratories, but their purposes and applications differ significantly. The key difference lies in the role of the additives (or the absence thereof) inside the tubes.
A plain tube is used when serum is needed for testing, and it allows blood to clot naturally. As mentioned, plain serum tubes are used for tests requiring serum, such as metabolic or liver function tests. On the other hand, an EDTA tube contains the anticoagulant EDTA (Ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid), which prevents blood from clotting. This makes EDTA tubes ideal for tests that require plasma or whole blood, such as complete blood counts (CBC), blood typing, or any tests requiring cellular components of the blood.
One of the primary distinctions between plain tube and EDTA tube is that EDTA tubes are designed for tests where the blood must remain in its liquid form without clotting. Conversely, plain tubes are used to collect blood that will be allowed to clot so that the serum can be separated for analysis.
Plain Tube Clot Activator
Some plain tubes are equipped with a clot activator to expedite the clotting process. These plain tube clot activator tubes contain a special additive that triggers the clotting of blood faster than a standard plain tube. The clot activator ensures that the blood clots more quickly, reducing the waiting time before centrifugation. This is especially helpful in situations where rapid serum collection is required, such as in emergency settings or when time-sensitive tests are needed.
The presence of the clot activator in the plain tube allows for a more efficient separation of serum from blood cells. After the blood has clotted, the tube is centrifuged, and the serum can be easily separated for analysis. These tubes are commonly used for blood chemistry tests and hormone level assessments, where the serum is the preferred sample.
Applications and Uses of Plain Serum Tubes in Laboratory Testing
Plain Tube Serum
The plain tube serum is a critical component in many laboratory tests that require serum rather than plasma or whole blood. Plain serum tubes are widely used for tests like blood chemistry panels, liver and kidney function tests, and tests for specific proteins, antibodies, or hormones. The serum obtained from these tubes is a clear, straw-colored liquid that is free of cells and other solid components after centrifugation. This makes it ideal for testing the concentration of various analytes in the blood.
Serum is often used to test for markers of disease or to monitor the levels of substances such as electrolytes, glucose, cholesterol, and other biochemical markers. For instance, plain tube serum is typically used for tests related to metabolic diseases, autoimmune disorders, and infections.
Plain Tube Used For
The plain tube used for blood collection is suitable for any situation where the analysis of serum is required. Some of the most common uses of plain tubes include:
Blood Chemistry Tests: These tests often require serum, which is the liquid part of blood after clotting. Plain tubes allow for the collection of serum, which can then be analyzed for various biochemical markers.
Hormone Level Testing: Hormones like thyroid hormones, cortisol, and insulin are commonly measured using serum obtained from plain tubes. The serum sample is crucial for the accurate measurement of these substances.
Liver and Kidney Function Tests: Serum is used to measure enzymes, proteins, and other markers associated with liver and kidney function. The plain tube is ideal for these tests, which can provide valuable insights into a patient's health.
Serological Testing: Tests that detect antibodies or antigens in the blood require serum samples, making the plain tube essential in the diagnosis of infections or immune system disorders.
The plain serum tube is an essential tool in clinical and laboratory settings, offering valuable benefits for blood collection and testing. Whether it is a plain serum blood tube, plain tube clot activator, or a standard plain tube used for serum collection, these tubes are designed to ensure that blood samples can be processed correctly for a wide variety of diagnostic tests. The ability of plain tubes to allow blood to clot naturally and separate serum makes them indispensable for tests ranging from blood chemistry panels to hormone level testing.
Understanding the differences between plain tubes and other types of blood collection tubes, such as EDTA tubes, ensures that healthcare providers and laboratory technicians can select the right tools for each test, ultimately leading to more accurate and reliable patient results.
-
Warmth That Heals: The Healthcare Benefits of Fleece Electric Blankets
NewsMay.26,2025 -
Vacuum Blood Collection Tubes: Essential Tools in Modern Hematology
NewsMay.26,2025 -
Understanding the ESR Test: Tube Type, Anticoagulant, and Pricing Insights
NewsMay.26,2025 -
Understanding Blood Collection Tubes: Focus on Plain Tubes and EDTA Tubes
NewsMay.26,2025 -
Therapeutic Warmth: The Healthcare Benefits of Electric Blankets
NewsMay.26,2025 -
Healing Heat: The Healthcare Advantages of Electric Blankets
NewsMay.26,2025