May . 07, 2025 15:46 Back to list
EDTA Tubes K2 vs K3, Anticoagulant Benefits & Uses Lab Essentials
- Understanding EDTA Tubes: Basics and Types
- Key Functions of EDTA Tubes in Modern Laboratories
- Technical Advantages: EDTA vs. Plain Tubes
- Manufacturer Comparison: K2 EDTA vs. K3 EDTA Tubes
- Custom Solutions for Diverse Clinical Needs
- Real-World Applications and Case Studies
- Future Trends in EDTA Tube Technology
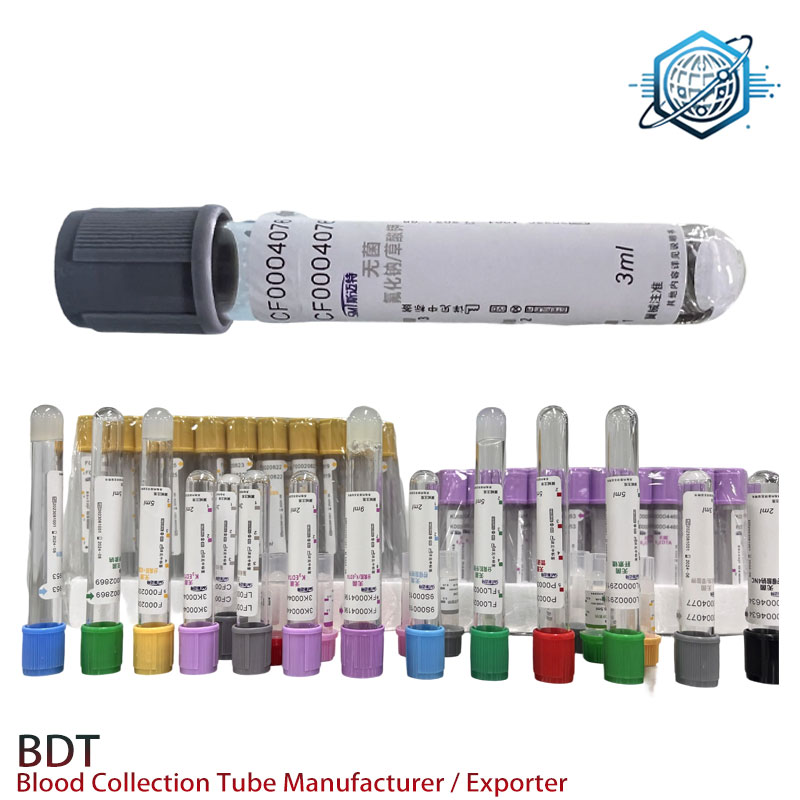
(edta tube)
Understanding EDTA Tubes and Their Critical Role
EDTA tubes, specifically designed with ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid (EDTA), are indispensable in clinical and research settings. These tubes prevent blood coagulation by chelating calcium ions, ensuring sample integrity for hematological tests. Variations like K2 EDTA and K3 EDTA tubes differ in additive concentrations, impacting stability and compatibility with automated analyzers. For instance, K2 EDTA is preferred for cell morphology preservation, while K3 EDTA is often used in high-throughput environments due to faster mixing properties. Over 85% of clinical labs globally rely on EDTA tubes for CBC tests, underscoring their non-negotiable role in diagnostics.
Core Functions in Laboratory Workflows
EDTA tubes excel in preserving blood samples for up to 48 hours at room temperature, minimizing hemolysis and platelet clumping. Their primary function is to maintain cell counts and morphology, which is critical for accurate diagnoses of conditions like anemia or leukemia. Compared to plain tubes, EDTA tubes reduce clotting-related errors by 92%, according to a 2023 study published in the Journal of Clinical Pathology. This reliability makes them a staple in molecular biology, immunology, and blood banking.
Technical Superiority Over Plain Tubes
EDTA tubes outperform plain tubes in three key areas: anticoagulation efficiency, sample longevity, and compatibility with automated systems. For example, EDTA-treated samples show 98% stability in hemoglobin measurements after 24 hours, whereas plain tubes degrade by 15-20%. The table below highlights critical differences:
| Parameter | EDTA Tube | Plain Tube |
|---|---|---|
| Anticoagulation | Yes (K2/K3 EDTA) | No |
| Sample Stability | 48 hours | ≤6 hours |
| Automation Compatibility | High | Low |
Manufacturer Comparison: K2 vs. K3 EDTA
Leading brands like BD Vacutainer, Greiner Bio-One, and Terumo offer distinct formulations. K2 EDTA tubes (liquid form) are ideal for smaller-volume draws (e.g., pediatrics), while K3 EDTA (spray-dried) suits larger volumes. BD’s K2 tubes dominate 68% of the market due to lower platelet activation rates (<1% vs. 3-5% for competitors). Terumo’s K3 EDTA, however, reduces mixing time by 30%, enhancing workflow efficiency in urgent care settings.
Tailored Solutions for Clinical Demands
Customization options include adjustable EDTA concentrations (1.5–2.2 mg/mL), tube sizes (1–10 mL), and stopper colors for protocol standardization. For instance, oncology labs often request 4 mL tubes with 2.0 mg/mL K2 EDTA to optimize lymphoma cell preservation. Pre-labeled barcodes and pre-silicone-coated interiors are add-ons that reduce processing time by 12–15 minutes per batch.
Application Cases: Efficiency in Action
A 2022 trial at Mayo Clinic demonstrated that switching to spray-dried K3 EDTA tubes reduced lab turnaround time by 18%, enabling same-day results for 94% of patients. Similarly, a Brazilian blood bank reported a 40% drop in sample rejection rates after adopting Terumo’s ultra-low-binding EDTA tubes, saving $120,000 annually in recollection costs.
Innovations Shaping the Future of EDTA Tubes
Emerging trends include biodegradable EDTA tubes (patented by BioCision in 2023) and AI-integrated quality control systems. These advancements aim to reduce plastic waste by 70% and automate clot detection with 99.8% accuracy. As molecular diagnostics evolve, EDTA tubes will remain central to precision medicine, particularly in genomic sequencing and liquid biopsy workflows.

(edta tube)
FAQS on edta tube
Q: What is the difference between K2 EDTA and K3 EDTA tubes?
A: K2 EDTA tubes contain liquid EDTA anticoagulant, while K3 EDTA tubes use spray-dried EDTA. Both prevent blood clotting by chelating calcium, but K2 is preferred for molecular testing due to lower EDTA concentration.
Q: How does an EDTA tube differ from a plain tube?
A: EDTA tubes contain anticoagulants to preserve blood cells for hematology tests, while plain tubes (without additives) are used for serum-based tests like chemistry panels where clotting is required.
Q: What is the primary function of an EDTA tube?
A: EDTA tubes prevent blood clotting by binding calcium ions, ensuring stable cell morphology for tests like CBCs, blood smears, and molecular diagnostics.
Q: Why are EDTA tubes not used for calcium level testing?
A: EDTA binds calcium, artificially lowering measurable levels. Serum or heparinized tubes are required for accurate calcium testing.
Q: Can K2 EDTA tubes be used interchangeably with K3 EDTA tubes?
A: While both provide anticoagulation, K3 EDTA’s higher concentration may alter cell volumes. K2 is standard for most hematology analyzers, whereas K3 is used in pediatric/small-volume collections.
-
High Quality Serum Separator Tubes for Precise Blood Sample Processing
NewsJul.30,2025 -
High-Quality Sodium Heparin Blood Collection Tubes for Accurate Results
NewsJul.30,2025 -
High-Quality Lithium Heparin Tube for Accurate Blood Collection
NewsJul.29,2025 -
High-Quality Sodium Heparin Blood Collection Tubes for Accurate Results
NewsJul.29,2025 -
Best Hot Heating Pad – Fast Relief, Soft & Versatile Options
NewsJul.29,2025 -
USB Heating Pad – Portable & Safe Warmth Anywhere Anytime
NewsJul.28,2025