- bdttonyjiao@hotmail.com
- +86 +8615081115902
- 9-1-701 TonfuTown Thành phố Thạch Gia Trang Tỉnh Hà Bắc Trung Quốc
Th5 . 16, 2025 14:40 Quay lại danh sách
The Essential Guide to Vacuum Containers for Blood Draw
Blood collection is a fundamental procedure in medical diagnostics, playing a crucial role in detecting diseases, monitoring health, and guiding treatment decisions. Among the tools that have revolutionized blood collection is the vacuum container for blood. This device has made blood draws more efficient, safe, and less painful for patients. In this article, we will explore the significance of vacuum containers for blood, the mechanics behind the vacuum for blood draw, and the best practices for their use in clinical settings.
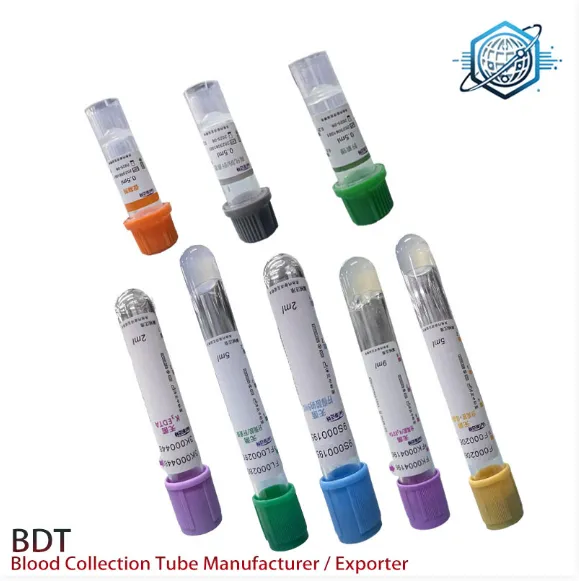

Understanding the Vacuum Container Blood: What It Is and Why It Matters
A vacuum container blood system, often referred to as a vacuum tube or evacuated tube, is a sterile glass or plastic tube with a rubber stopper. The tube is pre-evacuated, meaning it contains a vacuum that facilitates the automatic drawing of blood once a needle punctures the patient's vein and the tube is connected.
The main advantages of using a vacuum container for blood collection include:
Safety: The closed system reduces the risk of blood exposure and contamination for healthcare workers.
Efficiency: Blood flows directly into the tube, reducing the need for manual suction and minimizing discomfort.
Standardization: Tubes come with specific additives that preserve blood components or prepare samples for different tests.
Before the introduction of vacuum tubes, blood draws required syringes and manual aspiration, which were more cumbersome and riskier. The vacuum container blood system streamlined this process, making it the gold standard in blood collection.
How the Vacuum for Blood Draw Works: Mechanics and Components
The principle behind the vacuum for blood draw is simple yet effective. The vacuum inside the tube creates a pressure difference that pulls blood from the vein into the container once the vein is accessed. Here is a breakdown of the components and the process:
Vacuum Tube: This is the blood container with a predefined vacuum level. The vacuum ensures consistent blood volume is drawn, regardless of the patient’s vein pressure.
Needle Assembly: A double-ended needle is used, with one end inserted into the patient’s vein and the other puncturing the tube’s rubber stopper.
Holder or Adapter: This plastic device holds the tube and needle together, allowing easy insertion and removal of tubes during multi-sample blood draws.
Process:
The healthcare worker inserts the needle into the patient’s vein.
A vacuum tube is pushed into the holder, causing the needle to pierce the tube’s rubber stopper.
Blood is drawn automatically by the vacuum pressure into the tube.
Once the tube fills, it is removed, and another tube can be inserted if multiple samples are needed.
This system reduces the manual effort needed, decreases patient discomfort, and minimizes the risk of exposure to bloodborne pathogens.
Best Practices for Using Vacuum Containers for Blood Draw: Safety and Quality
While the vacuum container for blood draw system offers many benefits, proper usage and handling are essential to ensure patient safety and sample quality. Here are key best practices:
Selecting the Right Tube: Tubes come with different color-coded stoppers, indicating various additives such as anticoagulants (e.g., EDTA, heparin) or clot activators. Choosing the correct tube for the required test is crucial.
Maintaining Sterility: Use sterile equipment and avoid touching the needle or stopper to prevent contamination.
Proper Insertion Technique: Ensure the needle is correctly inserted into the vein to minimize patient discomfort and avoid complications like hematoma.
Correct Tube Filling: Tubes are designed to fill to a specific volume. Underfilling or overfilling can affect test results.
Labeling and Handling: Immediately label tubes after collection with patient information to prevent mix-ups. Store and transport tubes according to the test requirements.
In addition to these practices, proper disposal of used needles and tubes in sharps containers is vital for infection control.
The vacuum container for blood and the vacuum for blood draw technology have transformed blood collection into a safer, faster, and more reliable procedure. Understanding how these systems work and following best practices can significantly improve patient experience and diagnostic accuracy. For healthcare providers, mastering the use of vacuum containers is essential in delivering high-quality care in any clinical environment.
-
The Ultimate Guide to Choosing the Safest Cat Heating Pad
Tin tứcJul.25,2025 -
The Science Behind Self-Heating Pet Mat
Tin tứcJul.25,2025 -
The Science Behind Salt Heaters
Tin tứcJul.25,2025 -
The Perfect Temperature: How Reptile Heat Mats Improve Pet Health
Tin tứcJul.25,2025 -
The Cozy Canine: How a Dog Heating Pad Keeps Pets Warm
Tin tứcJul.25,2025 -
Pet Heating Pad: The Ultimate Guide
Tin tứcJul.25,2025